
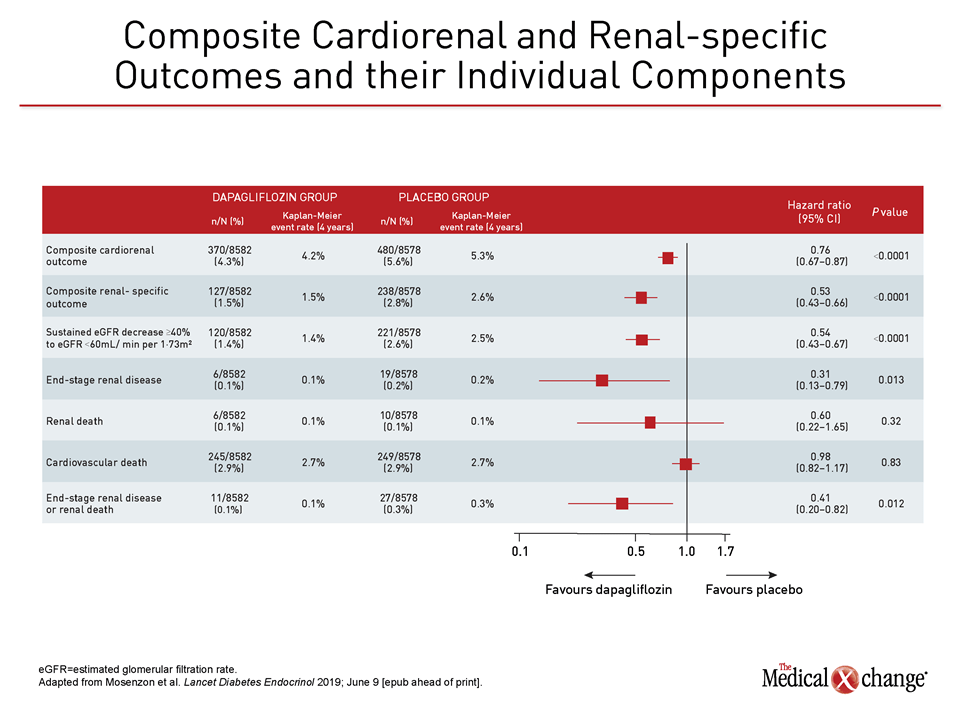
Meaning In this study, the effect of dapagliflozin on the relative risk for CV events was consistent across kidney function and albuminuria status, with the greatest absolute benefit for the composite of CV death or HHF observed among patients with both reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria. However, the absolute risk reduction of CV death and HHF was significantly larger for dapagliflozin-treated patients who had more markers of chronic kidney disease. Question What is the relative cardiovascular (CV) efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin according to the baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes?įindings In this secondary analysis of 17 160 participants included in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial, the effect of dapagliflozin (vs placebo) on the relative risk of a composite of CV death and hospitalization for heart failure (HHF) and of major adverse cardiovascular events was similar.
There were no significant differences between TNK and tPA with regard to mortality or reinfarction. Overall, rates of intracranial hemorrhage were 1.0% for 30 mg TNK, 1.9% for 40 mg TNK, 3.8% for 50 mg TNK, and 1.9% for tPA. There was a dose-response relationship between TNK dosing and serious bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage (the 50 mg dose of TNK was suspended due to three intracranial hemorrhages in patients treated with that dose). The half-life of TNK was longer than that of TPA, and there was less fibrinogen depletion with TNK. Similar results were seen when the endpoint of combined TIMI 2 or 3 flow was compared, and there were no differences seen when the analyses were compared before and after the protocol amendment (lowering the dose of heparin) was made. 62.7% for tPA, p=NS), but the 30 mg dose had a lower rate of TIMI 3 flow (54.3%, p=0.035 for comparison with tPA). TNK 40 mg and 50 mg produced similar rates of TIMI 3 flow to tPA (62.8% for 40 mg dose and 65.8% for 50 mg dose vs. The median time from onset of symptoms to treatment was 2.9 hours, and the groups were well-balanced overall. Patients undergoing rescue percutaneous coronary intervention had activated clotting times titrated to 300 seconds, with additional bolus heparin.Ī total of 886 patients were randomized. Heparin dosing was initially at the physician’s discretion based on a nomogram, but an amendment to the protocol instituted after supratherapeutic heparin doses was found and specified a weight-based dosing (for >67 kg, 5000 U bolus and 1000 U/h infusion for ≤67 kg, 4000 U bolus, and 800 U/h infusion). Concomitant Medications:Īspirin and Heparin. The 50 mg dose of TNK was suspended during the course of the trial, and a TNK 40 mg bolus arm was added, due to the recommendation of the Data Safety and Monitoring Board. Rate of TIMI 3 grade flow at 60 and 75 minutes, TIMI 2 or 3 flow at all time points, pharmacokinetics, coagulation parameters, recurrent MI, and serious bleeding Drug/Procedures Used:Īt the start of the trial, there were three arms: TNK 30 mg bolus, TNK 50 mg bolus, and front-loaded tPA (0.75 mg/kg up to 50 mg over 30 minutes, followed by 0.5 mg/kg up to 35 mg over 60 minutes). Rate of TIMI 3 grade flow at 90 minutes Secondary Endpoints:

The use of abciximab within the preceding 96 hours was added in an amendment.
Prior stroke, transient ischemic attack, or central nervous system structural damage history of dementia or major cognitive deficit blood pressure >180/110 mm Hg significant bleeding disorder within six months cardiogenic shock treatment of acute MI with thrombolytic therapy within the previous four days major surgery, biopsy, or trauma (including head trauma associated with the presenting MI) within three months prolonged (>2 minutes) cardiopulmonary resuscitation within two weeks recent noncompressible vascular puncture previous coronary artery bypass graft inability to undergo cardiac catheterization therapeutic oral anticoagulation pregnancy, lactation, or women of childbearing potential not using adequate birth control allergy to heparin or history of multiple allergies cocaine abuse other serious illness participation in another protocol previous treatment with TNK-tPA inability to follow the protocol or any other condition that the investigator felt would pose a significant hazard to the patient.
#Timi trials trial
An amendment during the trial added an upper age limit of 80 years. Presence of ischemic pain lasting ≥30 minutes, associated with ST-segment elevation ≥0.1 mV in ≥2 contiguous leads, and the ability to be randomized within 12 hours of symptom onset.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
